Parts of a Boat Spit: Essential Components and Functions Explained
Boating enthusiasts, whether they are beginners or seasoned sailors, need to understand the various parts of a boat and their functions. Knowledge of boat anatomy helps with navigation, safety, and overall enjoyment of time spent on the water.
In this article, we'll explore the essential components of a boat, their roles, and how they contribute to a successful and enjoyable boating experience.
From the bow to the stern, each part of a boat serves a specific purpose. The boat's structure, navigational components, and safety features ensure stability and ease of use.
For those planning to spend extended periods on the water, living quarters and deck features provide comfort and convenience. Boating enthusiasts might also be interested in propulsion systems, mooring and docking equipment, fishing amenities, and boat customization options.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding boat anatomy improves navigation, safety, and enjoyment on the water.
- Essential components include boat structure, navigational tools, and safety features.
- Additional amenities such as living quarters, fishing equipment, and customization options enhance the boating experience.
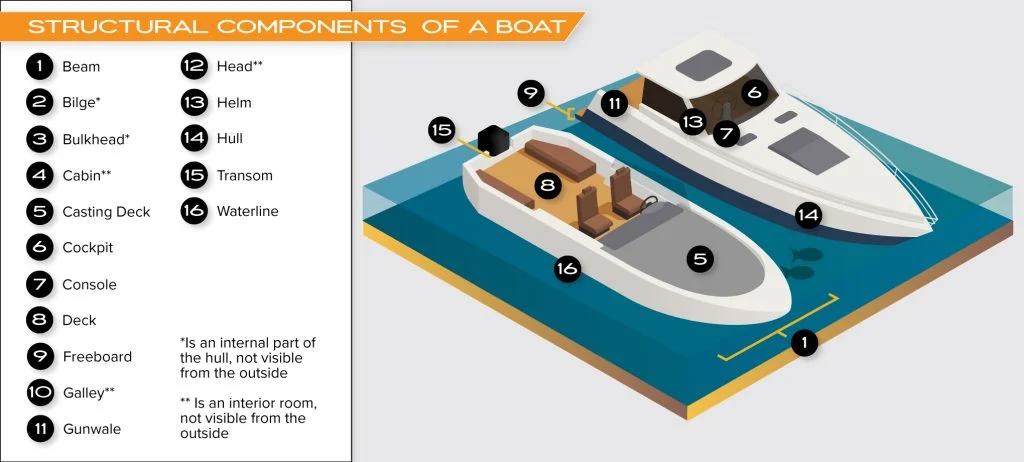
Basics of Boat Anatomy
Hull and Design
The hull is the main body or shell of a boat. It provides the primary structure and is designed to float and move efficiently through the water.
The shape and materials used in the hull's construction are critical to the vessel's performance and stability. The area where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline.
Hull design types vary based on the intended use of the boat. Some common designs include:
- Displacement Hulls: Designed to move through the water by displacing it, these hulls offer a smooth and stable ride, making them ideal for long-distance cruising.
- Planing Hulls: Capable of lifting the boat out of the water at high speeds, reducing resistance and providing a faster ride.
- Semi-Displacement Hulls: These offer a combination of displacement and planing hull characteristics, providing both stability and speed.
Boat Terms and Orientation
In addition to the hull, a boat consists of many other parts and components that contribute to its overall anatomy. Understanding these terms is essential for any boater:
- Bow: The front part of the vessel.
- Stern: The rear part of the boat.
- Port: The left side of the boat when facing the bow.
- Starboard: The right side of the boat when facing the bow.
- Deck: The surface on top of the hull that individuals can walk on.
- Cabin: An enclosed space within the boat, often used for sleeping or shelter.
- Bilge: The lowest internal part of the hull where water can collect.
- Transom: The cross-section of the boat at the rear, often used for mounting engines or other equipment.
Boat orientation is crucial for navigation and communication while on the water. By understanding the anatomy of a boat, boaters can communicate effectively and operate their vessels with confidence and clarity.
Boat Structure
Front and Back
The bow refers to the front of a boat, while the stern is the rear. Moving in the forward direction is going towards the bow, and moving aft means moving towards the stern.
The transom is a key structural component found at the cross-section of the rear of the boat.
An anchor is an essential device used for securing a boat, which is typically found stored near the bow when not deployed.
It plays a crucial role in holding the boat in a fixed position, even in rough waters, by attaching to the seabed.
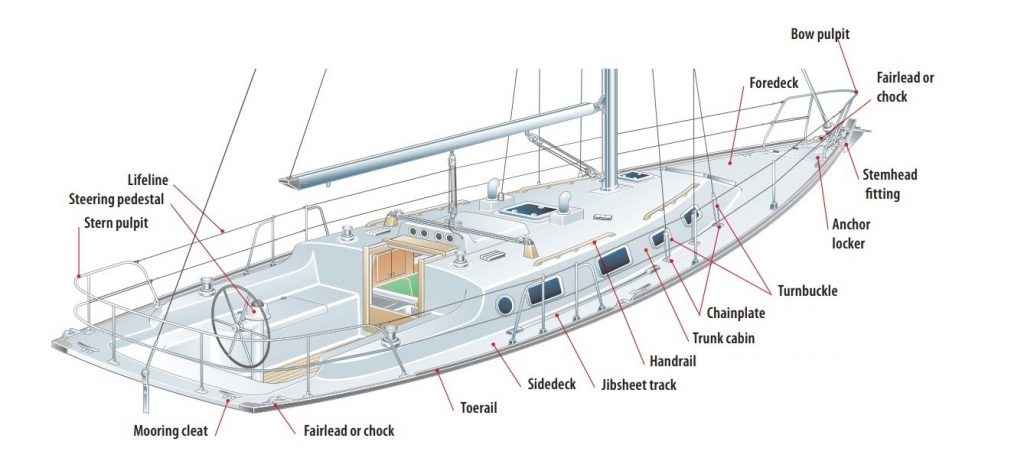
Deck Layout
The deck of a boat is the horizontal platform forming the primary working surface, roof, and reinforcement for the hull. It serves both functional and aesthetic purposes.
The superstructure includes elements located above the deck, such as the cabin, wheelhouse, and other components.
Various parts of the deck layout are described below:
- Foredeck: Area of the deck near the bow
- Main deck: Central portion of the deck
- Aft deck: Rear section of the deck
Boat decks can feature various elements, including seating areas, storage compartments, and navigation equipment. They are designed to accommodate the needs and preferences of the boat owner and the specific type of boat.
Navigational Components
Steering Mechanisms
The steering mechanisms on a boat are pivotal to navigating waterways efficiently and safely. A key element is the helm, which serves as the driver's seat and typically houses the wheel and throttle controls.
The wheel allows the operator to control the direction of the boat by turning the rudder located at the stern. Meanwhile, the throttle is important for regulating the boat's speed and managing engine power.
Another essential aspect to consider are the navigation lights.
These lights help signal the boat's position to other vessels, promoting safety when navigating during low visibility or nighttime conditions.
Sail and Mast Structure
A sailing boat's propulsion relies on the efficiency and proper set-up of its sail and mast structure.
Specifically, it comprises the sails which catch the wind to propel the boat, and the mast which supports the rigging and sail.
Rigging includes various ropes, cables, or chains used to hold up and control the sails.
It is essential to maintain and adjust these parts properly to optimize the boat's performance and ensure safe sailing.
Different types of sails include:
- Mainsail: The primary and largest sail, typically located behind the mast.
- Jib: A smaller triangular sail, positioned forward of the mast.
- Spinnaker: A large, lightweight sail used for sailing downwind.
When it comes to mast types, they can be:
- Single-masted: Featuring only one mast, as seen in sloop or cutter sailboats.
- Multi-masted: Offering more than one mast, found on ketches, yawls, or schooners.
Boat Safety and Stability
Buoyancy and Ballast
Boats rely on buoyancy for their function, which depends on the boat's hull design. The hull should have an appropriate shape to displace water and maintain its equilibrium.
Ballast is a critical aspect of stability, as it helps to counterbalance and distribute the weight of the boat.
The bilge houses the bilge pumps and plays a vital role in removing accumulated water, ensuring that the boat does not take on excessive water and sink.
In sailboats, additional stability may be achieved through the use of a weighted keel or a heavy centerboard.
Safety Features
Boats come equipped with several safety features designed to protect passengers and maintain stability. Here are a few of the essential safety features:
- Fenders: Fenders are cushion-like objects that absorb impact and protect the vessel from potential damage when docking or coming in contact with other boats. They are positioned on the sides of the boat.
- Cleats: Cleats are metal fittings attached to the deck, used for securing lines and ropes during docking or other boating activities. They ensure proper tension and provide a means to hold the vessel steadily.
- Life Jackets: These essential personal flotation devices increase the chance of survival if passengers end up in the water. Life jackets should always be worn and readily available for every person aboard.
- Fire Extinguishers: In case of onboard fires, fire extinguishers should always be present and easily accessible.
- Boat Stabilizers: As mentioned in this resource, boat stabilizers are essential for maintaining a level vessel, decreasing fuel consumption, and enhancing passenger comfort.
Ensuring that your boat has the necessary safety features and effectively handles buoyancy and ballast will contribute to a safer and more enjoyable boating experience.
Regular inspection of these features and educating passengers about their use is crucial for maintaining safety on the water.
Living Quarters
When it comes to living quarters on a boat, it is essential to understand the various parts and facilities that provide comfort and convenience for those onboard. This section will discuss the common onboard facilities and storage and comfort areas on a boat.
Common Onboard Facilities
The cabin serves as the private living space on a boat, usually located below deck. Cabins typically include essential amenities such as a bed known as a berth, storage options, and sometimes, a small table or dinette.
Boat cabins can vary in size and luxury, depending on the boat type and owner's preferences.
Boats often provide a galley or kitchen area, equipped with basic appliances allowing for food preparation and cooking. This space may include counter space, a stove, oven, refrigerator, sink, and storage for cooking utensils and supplies.
Boats additionally offer a heads or bathroom area, which typically features a marine toilet and sometimes a sink and shower. These facilities can range from compact and functional to spacious and luxurious, depending on the boat's overall design and purpose.
Storage and Comfort Areas
Boat storage and comfort areas ensure that passengers have the necessary space and amenities to make their stay aboard the vessel enjoyable.
In addition to the cabin's sleeping and storage areas, boats often have a saloon. The saloon provides a communal living area where passengers can relax, dine, and socialize.
This space often includes a larger table, comfortable seating, and sometimes entertainment options like a television or stereo system.
Storage solutions are crucial on a boat, given the limited space available.
Some boats feature built-in storage compartments and cabinets in various areas, including the cabin, galley, and saloon.
Additionally, storage spaces for essential gear like life jackets, ropes, and cleaning supplies are strategically placed throughout the vessel to maximize convenience and organization.
Deck Features
Entertainment and Leisure
One of the primary purposes of a boat deck is to provide a space for entertainment and leisure activities.
The cockpit serves as a central gathering area for passengers and often includes seating and dining arrangements.
The swim platform is an additional deck feature that extends from the stern of the boat, making it easy to access the water for swimming, snorkeling, or other water sports.
Another popular deck feature is the bimini, which is a canvas or fabric top providing shade and protection from the elements.
It is typically mounted on a metal frame attached to the boat and can be folded down when not in use.
Boats designed for fishing may have a casting deck at the bow or stern, offering a stable and elevated platform for anglers to cast their lines.
A sun deck is a dedicated area on the boat where passengers can relax and sunbathe.
They are usually equipped with comfortable lounging furniture and some boats may even have built-in cushioned seating, ensuring maximum relaxation for passengers.
Functional Deck Equipment
In addition to leisure activities, boat decks also serve functional purposes.
A hardtop is a solid, fixed roof structure found on some boats, providing more substantial protection and potentially allowing for additional equipment to be mounted, such as radar systems or fishing rod holders.
The canvas on a boat is used to cover and protect the boat when not in use. This helps to prevent damage caused by sun, rain, or other environmental factors.
Here's a brief list of some common deck equipment:
- Cleats: Used for securing ropes or lines.
- Anchors: Aid in keeping the boat in a fixed position when stopped.
- Winches: Facilitate raising, lowering, or adjusting sails on sailboats.
- Rails: Provide a barrier for safety and support around the perimeter of the deck.
Boat Propulsion
Motorized Components
Boat propulsion can be achieved through the use of motorized components, including engines and propellers.
Typically, motorized boats utilize either inboard or outboard engines depending on the boat's design. The choice between the two types of engines will affect the boat's overall performance and handling capabilities.
Inboard engines are located inside the boat's hull, whereas outboard motors are mounted on the transom, outside the boat.
They are more easily accessible for maintenance and have the advantage of being removable.
In both cases, a propeller is responsible for transferring the engine's power into thrust, propelling the boat through the water.
Propellers come in various designs and materials that can greatly impact a boat's performance.
Sailing Apparatus
For sailboats, propulsion is primarily achieved through a sailing apparatus which includes sails, masts, and rigging.
The most important sail on a sailboat is the mainsail, which provides the primary source of propulsion. It is attached to the mast and can be adjusted using various control lines or sheets.
In addition to the mainsail, sailboats may have one or more secondary sails:
- Jib: A triangular sail set forward of the main mast, providing balance and additional propulsion when sailing upwind.
- Spinnaker: A large, lightweight sail used when sailing downwind, increasing speed and performance.
As an alternative to engine-powered propulsion, the sailing apparatus relies on wind power, making it an environmentally friendly option. However, the performance of a sailboat will vary depending on wind conditions.
Mooring and Docking
Docking Hardware
When docking a boat, it is essential to use appropriate hardware to ensure safety and stability.
One critical component is the cleat. Cleats are metal fittings fixed to the boat and dock, providing secure attachment points for mooring lines.
Boats over 55 feet usually have four cleats (two bow cleats and two stern cleats) and a couple of additional ones between them for spring lines.
Dock lines are ropes that secure the boat to the cleat on the dock. They come in various materials, such as nylon, polyester, and polypropylene, of which nylon is the most popular due to its strength and elasticity.
It is essential to choose the right dock line diameter according to your boat's size and weight.
Mooring Techniques
When anchoring, several techniques and principles should be followed to ensure the safety of your boat.
Firstly, choose a safe area considering factors such as boat traffic, obstacles, wind, and current.
Then, securely attach the inboard end of the anchor line to your boat and the outboard end to the anchor.
Slowly lower the anchor into the water until it reaches the bottom.
In addition to anchoring, there are other methods for securing your boat, such as using mooring buoys.
Mooring buoys are usually anchored to the sea floor and are used to attach the mooring lines from your boat.
This setup acts similarly to an anchored boat, keeping it in place while preventing direct contact with the dock.
When mooring, lines should be attached to both - the boat and dock.
A typical mooring setup involves the following types of lines:
- Bow lines: Attached to the bow cleats and extend forward from the boat.
- Stern lines: Attached to the stern cleats and extend aft from the boat.
- Spring lines: Attached to the midship cleats and run both forward and aft to prevent forward and aft movement.
Fishing Amenities
Essential Fishing Gear
A well-equipped boat should include some essential fishing gear to enhance your experience.
One such indispensable amenity is a livewell. A livewell is a built-in tank that stores fish caught until the end of your trip.
It provides the necessary water circulation and oxygen supply to keep the fish alive while on board.
Another useful addition is a bait tank. A bait tank is a container designed to hold live bait, maintaining water temperature, and oxygen levels.
Fishing enthusiasts widely use this feature as it keeps bait fresh and thus more appealing to the fish.
Fishing rod holders are a crucial accessory for anglers.
They secure your rods, making it convenient for trolling or managing multiple lines while fishing.
The holders also keep the rods out of the way and allow you to take a break.
A trolling motor is another essential for anglers, as it provides optimal boat control and quiet movement during fishing.
Trolling motors support precise and stealthy maneuvers in different fishing environments, allowing you to approach your target fish without scaring them away.
Fish Preservation
Once you've caught a fish, preserving its freshness is vital. Here are a few methods that can help:
- On ice: Storing fish on ice as soon as they are caught ensures freshness and maintains flavor. Make sure the ice is well-drained to avoid soaking the fish in water.
- In a cooler: A insulated bag or cooler is an appropriate means of storing fish during a fishing trip. Place fish in a cooler or insulated bag with ice to keep them fresh, and don't forget to drain the water.
- Using a Livewell: As mentioned earlier, a livewell serves as temporary storage for live fish. It maintains water temperature and oxygen to keep the fish alive for prolonged periods, ensuring top-quality seafood once you're back on land.
Boat Customization and Accessories
Comfort and Enhancement
One essential aspect of boat customization is enhancing the comfort level of your vessel.
Installing new seating options can make your time on the water more enjoyable for you and your passengers.
For instance, adding padded seats or benches can provide ultimate relaxation while cruising.
In addition to seating options, boat fenders and bumpers can protect your vessel from potential damage, ensuring both a safe and comfortable experience.
A good fender or bumper will help guard the hull and reduce impacts when docking.
A list of common comfort and enhancement accessories:
- Padded seats and benches
- Boat fenders and bumpers
- Custom storage solutions
- Cupholders and table installations
Boat Performance Add-ons
When considering boat performance add-ons, there are a variety of modifications and upgrades that can improve your vessel's maneuverability, speed, and overall efficiency.
For example, upgrading your propeller can lead to better performance and fuel economy.
Installing trim tabs can assist with balance and make your vessel more responsive to environmental conditions.
Incorporating a new sprit kit can also maximize your boat's sailing capabilities by efficiently managing sails and rigging systems.
Boat performance add-ons may include:
- Propeller upgrades
- Trim tab installation
- Sprit kit integration
- Advanced navigation systems
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the name for the rear section of a boat?
The rear section of a boat is called the stern.
How is the stern of a boat defined and what is its function?
The stern is the rear part of a boat, typically defined by the point where the hull meets the transom.
Its primary function is to provide stability and control the boat's direction while under movement, either by sailing or motor propulsion.
What components make up the spitting part of a boat?
There isn't a specific "spitting part" of a boat. However, this question may refer to the split between the boat's hull and deck, which are two essential components that make up the structure of a boat.
The hull is the main body that provides buoyancy and protection from water, whereas the deck is the flat surface above the hull supporting occupants and equipment.
Can you explain the term 'gunnel' in the context of boat parts?
A 'gunnel' (or 'gunwale') refers to the upper edge of a boat's side, providing structural support and reinforcement to the hull.
Gunwales often act as attachment points for ropes, cleats, and other essential boating equipment.
What is referred to as the tip of a boat, and what purpose does it serve?
The tip of a boat is commonly referred to as the bow, which is the front or forward part of the vessel.
The bow's design helps the boat cut through water, reducing resistance and allowing for smoother navigation.
Could you provide a clear diagram labeling the basic terminology of a boat's structure?
Unfortunately, we cannot directly include an image in this response. However, we recommend visiting this Boat Anatomy 101 article.
The article includes a valuable diagram to help you understand the basic terminology and structure of a boat's parts.
Charlie is Editor-in-Chief of Sea Magazine







